Abstract
This research paper is a proposed patient-centered educational brochure/pamphlet on the clinical manifestations of the common treatment options for hypothyroidism. One out of approximately three hundred persons in the United States has hypothyroidism. What is more, it is more common for females than males, and its prevalence may increase with age. Hypothyroidism is a clinical disorder and is diagnosed mostly by the primary care physicians. Untreated hypothyroidism contributes to such health deviations as cognitive impairment, dyslipidemia, hypertension, infertility, and neuromuscular dysfunction. Therefore, the particular brochure is designed for the use by nurse practitioners with their patients, who were newly diagnosed with the kind of disorder. The brochure contains information about the disorder, its development and symptoms. In addition, it informs about the possible methods of treatment and discusses common medications that the patient might be prescribed and any potential side effect patients need to be aware of.
Place New Order
Keywords: thyroid, hypothyroidism, medication, symptoms, malfunction
Hypothyroidism
What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a disease occurring when the thyroid endocrine gland starts to malfunction. The thyroid gland resembles a butterfly in its form (Picture 1), and is located in the lower part of [the] neck, in front of [the] windpipe (Shomon, 2009). Its name comes from the Greek word thyreoeides, which literally means shield-shaped (Shomon, 2009). The duty of the thyroid gland is to produce thyroid hormones, which are first secreted into the blood and then carried to every body tissue (American Thyroid Association, 2013). The hormone that the thyroid contains helps the organs, heart, brain, and muscles work in their usual manner and rhythm, use the body energy correctly and stay warm.
Picture 1. The Location of the Thyroid Gland
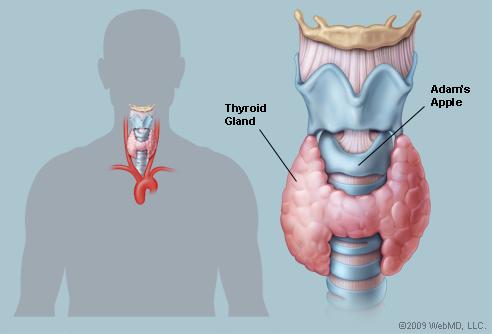
Hypothyroidism occurs when there is a primary gland failure or insufficient thyroid gland stimulation by the hypothalamus or pituitary gland (Gaitonde, Rowley & Sweeney, 2012). People, who suffer from hypothyroidism, have their thyroid gland not producing enough thyroid hormone to keep all the body functions in their vital and normal conditions. The low level of the thyroid hormone causes the slowdown of body functions, leading to such symptoms as dry skin, loss of energy, fatigue, memory problems etc (Table 1).
Table 1. Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
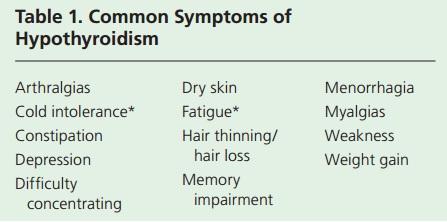
The severity of each of these symptoms may be reflected according to the degree of typhoid dysfunction and the concrete period of illness development and advancement. If the treatment is not applied immediately, the clinical symptoms will substitute the most common symptoms (Table 2).
Table 2. Clinical Signs of Hypothyroidism
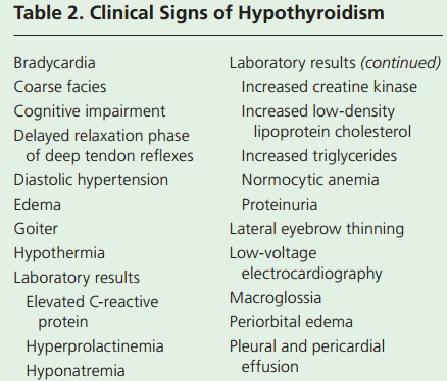
Patients with severe hypothyroidism will experience numerous clinical symptoms of this disease.
Who Can Develop Hypothyroidism?
Being the most common disease all over the world and affecting people of every age, race, sex, wealth status, and education, hypothyroidism with mild representation is diagnosed in 15% of Americans, and only 3% of these people have severe manifestations of the disease (American Thyroid Association, 2013). The majority of people, who are hypothyroidism-positive, are not even aware they have such an illness.
However, if one…
has a relative with an autoimmune disease;
is more than 45-50 years of age;
- Our custom writing services includes:
- Plagiarism and AI free custom writing for the best grades;
- CV, resume and cover letters which would
make you successful - Thesis and dissertations writing by academic
authors

is a woman (pregnant, after delivery, or around menopause);
is White or Asian;
has type I diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, celiac disease, Addisons disease, pernicious anemia, or vitiligo;
has been treated with radioactive iodine (neck and chest);
had a thyroid surgery
has genetic disorders (Down or Turner syndromes);
has a bi-polar disease (American Thyroid Association, 2013);
…the chances of having a hypothyroid disease are very high.
Diagnosing Hypothyroidism
In order to diagnose hypothyroidism, a physician takes into account the following factors:
the symptoms reported by the patient;
patients medical history and family history;
risk factors;
a physical exam;
a blood test TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) (Table 3) (American Thyroid Association, 2013).
Table 3. Screening and Diagnosing Hypothyroidism
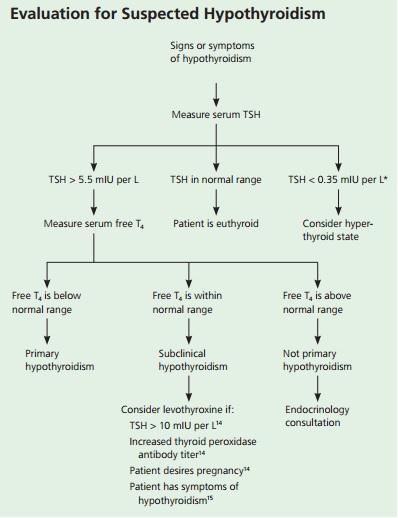
The aim of the blood test is to find out how much T4 is produced by the thyroid.
(Table 4. TSH (normal and abnormal indexes)

If the blood test shows TSH of an abnormally high level, it means that one has hypothyroidism (Table 4).
Hypothyroidism Treatment
Hypothyroidism can be treated and managed in most of the cases, but not completely cured. Most patients that have hypothyroidism will need to go through a long process of thyroid hormone therapy. The normally functioning thyroid gland makes two thyroid hormones (T4 and T3), and which should be substituted by a synthetic thyroxine hormone. The synthetic thyroxine must be taken on the daily basis and for life.
The primary care a doctor (or another practitioner) gives the newly diagnosed patients with hypothyroidism relying on:
weight;
age;
cause of hypothyroidism;
additional health conditions;
other medication the patient is taking (American Thyroid Association, 2013).
The most important fact in starting the treatment is that it can no longer be stopped. The dosage of thyroxine depends on the individual characteristics of the patient. Thyroxine is not an antibiotic and it does not cure hypothyroidism in two weeks and forever. If for some reasons the pill is not taken, hypothyroidism will return.
What are you waiting for?
Order with 15% discount NOW!

Those patients, who are hypothyroidism positive and refuse to be treated due to feeling fine, still need to be treated, because the illness progresses slowly and will result in the same consequences and further hospitalization.
Tips For Taking Thyroxine Pills
In order to form a healthy intake everyday habit, the patient needs to:
take the pill daily at the same time;
keep track of the pill intake by storing pills in containers marked for each day of the week;
store the pills in the place that is dry, out of childrens reach;
The pill can be taken with any liquid except soy milk, grapefruit juice and coffee;
The pill should not be swallowed without liquid as the dosage will dissolve in the mouth;
Wait approximately four hours after taking thyroxine if the food eaten had soy, or calcium supplements, iron supplements, antacids and other medicine (American Thyroid Association, 2013).
Treatment Side Effects
Despite the positive effect of thyroxine, it also can cause negative side reactions. If the dosage taken is too little, hypothyroidism will continue (American Thyroid Association, 2013). If the dosage taken is too high, thyroid may become overactive and cause hyperthyroidism. Therefore, the dose of thyroxine should be strictly adhered to.
